Overview
Map of Romania with Europe and CEE Region
Transylvania is a truly stunning scenic region with great history and heritage, which is found in central Romania, located in Central Europe.
Transylvania has the mighty Carpathian mountain range, and historical Transylvania extended westward to the Erdélyi- középhegység or Apuseni Mountains.
The term Transylvania is actually translated from its original Hungarian name – Erdély.
Its major capital city is Cluj-Napoca in Romanian, Kolozsvár in Hungarian and in German Klausenburg. Today the area covers an area of 100,290 km2 and is divided into 16 counties with in central and northwest Romania.
Current population in Transylvania is almost 6,8 inhabitants and the Major ethnic groups are: Romanians – 70 %, Hungarians – 20 %, Germans – 1 %, other ethnic groups make up last +/- 9 %.
Socio-Economic Profile
Several counties across Transylvania recorded some of the highest economic growth rates in Romania during 2016, ranging from 5.5% to 6.2%; while during 2017, seven Transylvanian counties had a GDP growth rate above the national average ranging between 3.3% and 4.8%. In 2017 – Although the population of Transylvania accounted for 34% of the total population of Romania; Transylvania produced about 32.4% of the national GDP.

During the same year, the Romanian GDP rose to 12.6% to $211.8 billion, while the GDP growth in Transylvania was higher at 13.3%.
Agriculture is an important, widespread occupation in the Transylvanian Plateau, with livestock farming, general agricultural produce production including various fruits and vegetables, and some wine production.
The agricultural produce incorporates various staple cereals, vegetables, viticulture, as well as cattle, sheep, swine, and poultry farming. The timber industry is another important natural resource.
Transylvania has always been known to be rich in mineral resources such as Gold, copper, iron, lignite, lead, manganese, natural gas, salt and sulfur. The corresponding heavy industries include sizeable iron and steel, chemical, and textile industries.
The electronics, automotive and IT sectors are important industries spread across Transylvania, and include many significant multinational companies such as: Bosch GmbH, Emerson Electric, Alcatel-Lucent, Flextronics and Continental AG.
Transylvania has had a rich medical tradition, with many well-established hospitals and medical training institutions.
The region has developed a strong industrial and services sector that produces trucks and buses, pharmaceuticals, natural gas, alcoholic beverages, fertilizers, and financial services.
Investment Opportunities
Investment opportunities range from Real Estate and Property development; Logistics and Office property; Infrastructure development; Agriculture and Value-Add products manufacturing; Tourism (including Agri-tourism, eco-adventure and sports tourism such as skiing, nature tourism, culture and heritage tourism); and other sectors such as mining.
Mining opportunities could still be re-activated in areas such as the Jiu Valley in the Hunedoara County / Hunyad megye, which had been a major mining area during the 19th century and the 20th century. Most mining operations had ceased after the collapse of the communist government, which compelled the region to try and diversify its economy.
Tourism
Tourism to Transylvania holds great promise and has steady attracted ever increasing numbers of curious visitors from across the World.
Transylvania is probably best known for medieval towns, mountainous borders and Gothic styled castles like those associated the legend of Dracula.
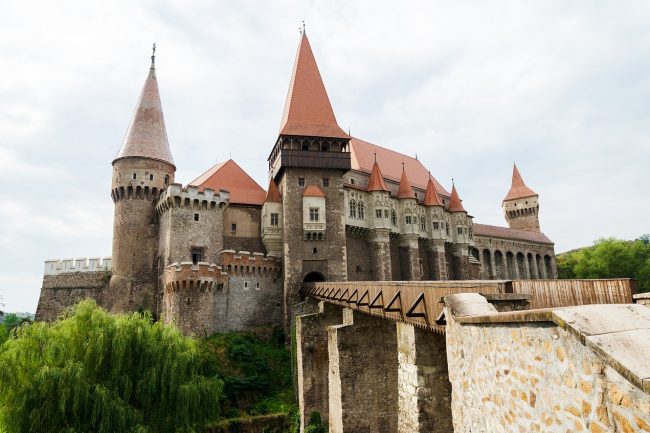

Castle of Vajdahunyad
The major cities include: Cluj-Napoca or Kolozsvár the de-facto Capital; Temesvár, Nagyvárad, Marosvásárhely, Brassó, Sighișoara or Schäßburg, Marosvásárhely, Sepsiszentgyörgy, Székelyudvarhely, Vajdahunyad, Temesvár, Arad, etc.
Apart from Romanian, Hungarian is the major language in eastern Transylvania, where it is widely spoken in many of the major cities, and the counties like the Harghita or Hargita megye. The reason for this is because Erdélyi or Transylvania was associated with Hungary for more than a thousand years, before being annexed to the Romanian Kingdom, after WWI. The ethnic Hungarians make up around 20% of the population of Transylvania, with almost half of these are Székely or Szeklers people. The Székely are believed to be descended from Attila’s Huns who settled in the Carpathian Basin in the 5th century.
During the 12th century Saxons merchants from Germany were settled in the region, after the Magyars had fought many wars of attrition against the Tatars and Turks. These German settlers built many fortress towns, identified as the Siebenbürgen, and hundreds of fortified churches. Unesco World Heritage Sites include many places with medieval Saxon architecture as in the city of Sighișoara or Schäßburg, Segesvár in Hungarian. Following the collapse of communism during 1989, almost 90% of these Germanic people left to West Germany.
There are many stunning cities with features ranging from Hungarian Gothic, neo-classical and expansive colorful baroque buildings, to Saxon walls and bastions, to Romanian styled architecture including towering Gothic Churches and courtyards.
There are unparalleled nature and eco-adventure sports opportunities across this region, including ever-more developing skiing resorts, across the mighty Carpathian mountain range.
Transylvania is less known for its wondrous therapeutic thermal mineral waters, which can be discovered throughout the region.
Nagyszeben (Sibiu, Hermannstadt), a city in central Romania, was voted among the best European destinations of 2020 in the European Best Destinations (EBD) competition.